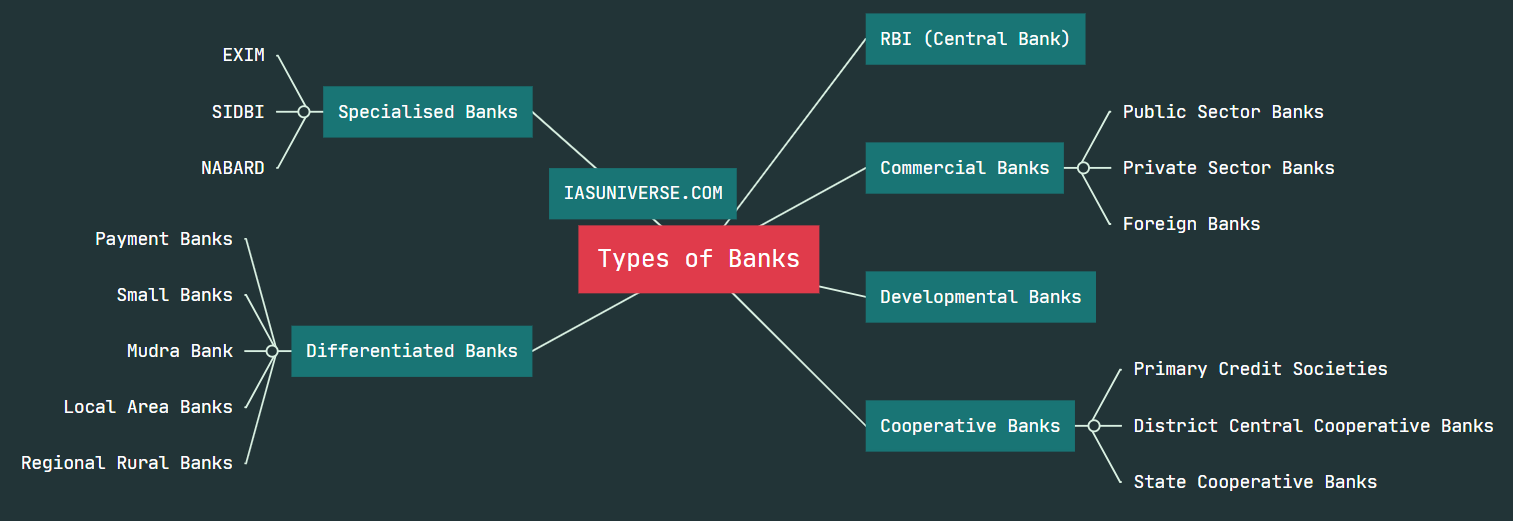
A Co-operative bank is a financial entity which belongs to its members, who are at the same time the owners and the customers of their bank. It is distinct from commercial banks.
They are broadly classified into Urban and Rural co-operative banks based on their region of operation.
They are registered under the Co-operative Societies Act of the State concerned or under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002.
- The Co-operative banks are also governed by the
- Banking Regulations Act, 1949.
- Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955.
Co-operative banks have a three tier structure—
(i) Primary Credit Societies–PCSs (agriculture or urban),
(ii) District Central Co-Operative Banks– DCCBs, and
(iii) State Co-Operative Banks-SCBc (at the apex level).
Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs):
1. Primary credit societies (PCSs) in urban areas that meet certain specified criteria can apply to RBI for a banking license to operate as urban co-operative banks (UCBs).
2. They are registered and governed under the co-operative societies acts of the respective states and are covered by the Banking Regulation Act, 1949—thus are under dual regulatory control.
3. The managerial aspects of these banks—registration, management, administration, recruitment, amalgamation, liquidation, etc. are controlled by the state governments, while the matters related to banking are regulated by RBI.
4. Well managed primary UCBs with deposits of over Rs. 50 crore are also allowed to operate in more than one state subject to certain norms.
UCBs and Multistate cooperative banks in news:
1. Recently, the Central government approved an Ordinance to bring all urban and multi-state co-operative banks under the direct supervision of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
2. The decision comes after several instances of fraud and serious financial irregularities, including the major scam at the Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative (PMC) Bank in 2019.
3. Till now, all the co-operative banks came under dual regulation of the RBI and the Registrar of Co-operative Societies, resulting in regulatory and supervisory lapses at many of these banks.
4. The RBI had no powers to draw up an enforceable scheme of reconstruction of a co-operative bank. However, from now onwards the urban and multi-state co-operative will come under the direct supervision of RBI.
5. Also, earlier the Supreme Court pronounced that co-operative banks come within the definition of ‘Banks’ under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 for the purposes of the Sarfaesi Act, 2002.
